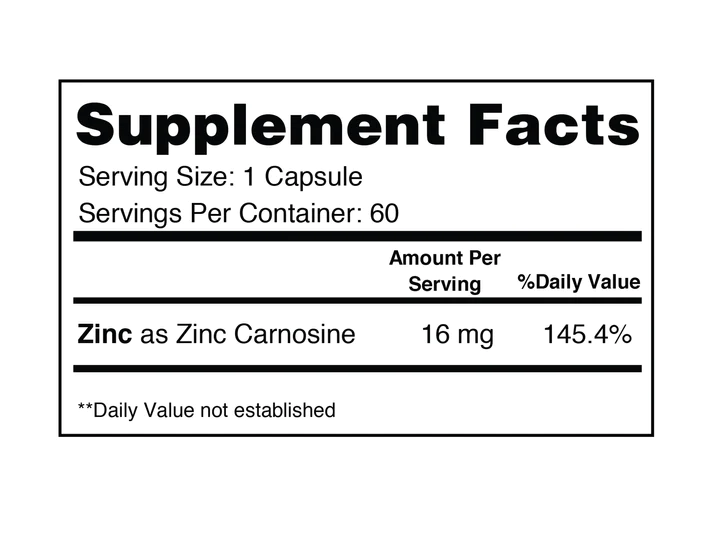
Description
Zinc is the second most abundantly distributed trace element in the body after iron.
Those that have been plant based (vegan or vegetarian) for several years are at greatest risk for zinc deficiency. It is found in nuts, seeds, and legumes, but those foods also contain phytic acid, which impair mineral absorption, namely zinc.
Even if it is in the food, you aren’t necessarily absorbing it…
Zinc absorption primarily takes place in the small intestine, and conditions that affect the function or integrity of the small intestine can lead to impaired zinc absorption. Some of these conditions include celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis), short bowel syndrome, chronic diarrhea, and cystic fibrosis.
If someone consumes one of the richest sources of zinc daily, red meat, it is still possible to be deficient in zinc because of intestinal disorders, cadmium exposure or even genetic mutations which prevent its absorption or transport into the cells.
While it is best known for its role in immune function, wound healing, and growth and development, there are several lesser-known health benefits of zinc..
BENEFITS OF ZINC:
- Cognitive function: Zinc is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, modulation of synaptic transmission, and brain development. Some studies have suggested that adequate zinc levels may support memory and learning.
- Vision: Zinc is present in high concentrations in the retina and is involved in the functioning of certain enzymes and proteins essential for vision. Adequate zinc intake may help maintain normal visual function and may play a role in preventing age-related macular degeneration.
- Fertility and reproduction: Zinc is important for both male and female reproductive health. In men, zinc is crucial for sperm production, testosterone synthesis, and prostate function. In women, zinc is involved in hormonal balance, egg development, and pregnancy maintenance.
- Taste and smell: Zinc is involved in the proper functioning of taste and smell receptors. Zinc deficiency can lead to a decrease in taste and smell sensitivity, which can be restored with zinc supplementation in some cases.
- Skin health: Zinc has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for skin health. It may help to reduce acne, inflammation, and the healing of skin lesions.
- Blood sugar regulation: Zinc is involved in insulin production, storage, and release, which are essential for blood sugar regulation. Adequate zinc levels may help maintain normal blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Bone health: Zinc plays a role in bone metabolism and mineralization, contributing to bone strength and integrity. Adequate zinc intake is necessary for maintaining bone health and preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
What makes this product unique is that it is bound to an amino acid called carnosine. Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) is a naturally occurring dipeptide found in high concentrations in muscle and brain tissues. It has a variety of potential health benefits due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-glycation properties.
BENEFITS OF CARNOSINE:
- Antioxidant properties: Carnosine has potent antioxidant properties, meaning it can neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. By doing so, it helps protect cells from oxidative stress and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and cancer.
- Anti-aging effects: Carnosine can inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are compounds that contribute to the aging process and the development of age-related diseases. By inhibiting AGE formation, carnosine may help slow down the aging process and prevent age-related cognitive decline.
- Neuroprotective effects: Carnosine has been shown to protect nerve cells from damage and promote their survival in various experimental models. It may have potential benefits in the prevention and management of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- Muscle health: Carnosine is found in high concentrations in skeletal muscles, where it may play a role in maintaining muscle function and reducing fatigue. Some studies suggest that carnosine supplementation may improve exercise performance and recovery in athletes.
- Cardiovascular health: Carnosine’s antioxidant and anti-glycation properties may contribute to improved cardiovascular health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in blood vessels, thereby reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and other heart-related conditions.
- Diabetes management: Carnosine’s anti-glycation properties may help in managing type 2 diabetes by reducing the formation of AGEs, which are associated with diabetic complications. Some studies suggest that carnosine supplementation may improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Wound healing: Carnosine has been shown to promote wound healing by reducing inflammation and promoting the growth of new blood vessels.
Zinc carnosine is created by combining one zinc ion with two molecules of carnosine. The combination of zinc with carnosine enhances the stability and bioavailability of both, allowing them to work synergistically in the body.
Zinc carnosine has been shown to have several health benefits, particularly related to gastrointestinal health.
BENEFITS OF ZINC CARNOSINE:
- Gastrointestinal health: Zinc carnosine has been found to be effective in supporting gastrointestinal health, particularly in the treatment of gastric ulcers and gastritis. It helps to protect the stomach lining and promote the healing of gastric mucosal lesions by enhancing mucus production, suppressing inflammation, and reducing oxidative stress.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Zinc carnosine has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for various inflammatory conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and gastritis.
- Antioxidant properties: Both zinc and carnosine have antioxidant properties, and the combination in zinc carnosine may provide enhanced protection against oxidative stress.
- Wound healing: Zinc carnosine may promote wound healing by supporting tissue repair and reducing inflammation, thanks to the combined effects of zinc and carnosine.
- Potential synergistic effects: The combination of zinc and carnosine in zinc carnosine may provide additional benefits by enhancing the bioavailability and stability of both compounds, allowing them to work more effectively together.
SUGGESTED USAGE:
Take one capsule once or twice daily with a meal.